What's the difference between NAS drives and standard HDDs?
Introduction:
NAS drives (Network-Attached Storage) and standard HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) are both storage devices used for storing and accessing data. Although they share some similarities, there are key differences that set them apart. Let's explore these differences to better understand their unique features and functionalities.
NAS Drives:
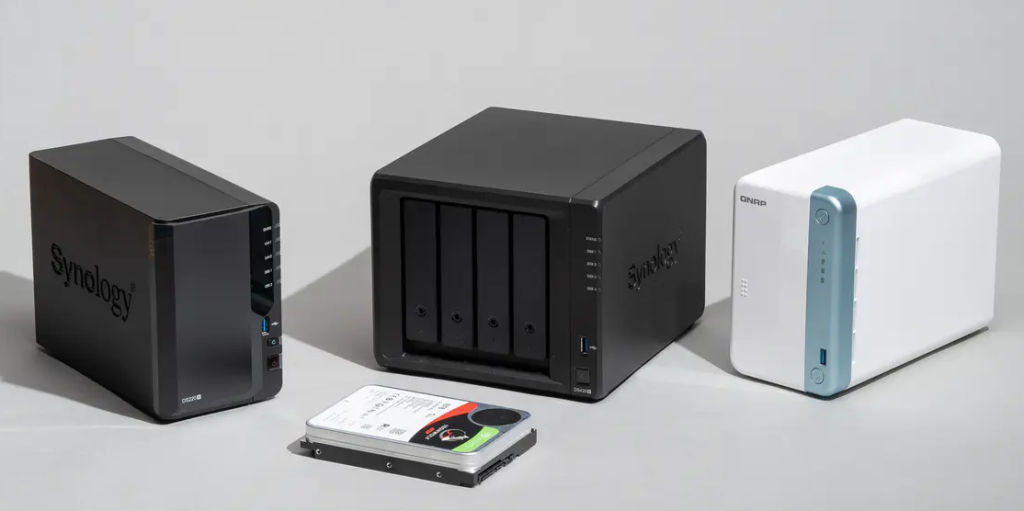
NAS drives are designed specifically for use in network environments, where multiple devices need to access and share data simultaneously. NAS drives connect directly to a network and are managed by a network operating system, providing centralized storage and file-sharing capabilities. They are typically equipped with their own processor, memory, and operating system, which enables them to perform various tasks independently. This setup allows NAS drives to function as dedicated file servers, capable of running applications and services like file syncing, media streaming, and even hosting websites.
Standard HDDs:
Standard HDDs, on the other hand, are traditional hard drives primarily used as internal storage in individual computers or laptops. They are connected directly to a computer's motherboard and rely on the computer's processor and memory to perform storage-related tasks. Standard HDDs have limited built-in networking capabilities and are not designed for shared access over a network. However, they offer high storage capacities and are cost-effective options for personal use or non-networked environments.
Differences:
The main differences between NAS drives and standard HDDs can be summarized as follows:
- Functionality: NAS drives provide advanced networking capabilities and are designed for multiple client access, whereas standard HDDs are primarily used for individual local storage.
- Network Connectivity: NAS drives have built-in network interfaces and can connect directly to a router or switch, while standard HDDs require a host computer to control access over a network.
- Independent Operation: NAS drives have their own processors, memory, and operating systems, allowing them to function independently as network storage devices. In contrast, standard HDDs rely on the processing power and memory of the host computer.
- Scalability: NAS drives offer scalability options, allowing users to easily expand storage capacity by adding additional drives or utilizing RAID configurations. Standard HDDs have limited scalability and often require replacing existing drives with larger ones.
- Redundancy and Data Protection: NAS drives often support features like RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), which offer data redundancy and protection against drive failures. Standard HDDs typically do not offer built-in redundancy options and may require additional measures for data protection.
In summary, NAS drives are specialized storage devices designed for network environments, providing advanced networking capabilities, independent operation, and scalability options. Standard HDDs, on the other hand, serve as traditional storage drives for individual computers with limited network functionality and lower scalability.