The Significance of RAID in NAS Configurations
In NAS (Network Attached Storage) configurations, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) plays a vital role in ensuring data integrity, reliability, and performance.
Redundancy and Data Protection
RAID provides a level of redundancy by distributing data across multiple hard drives, thereby protecting against data loss in case of drive failures. Various RAID configurations offer different levels of redundancy, such as RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10.
Improved Data Availability and Access Speed
With RAID, data access is not dependent on a single drive. Instead, it allows multiple drives to work together, increasing the aggregated read and write speeds. This results in improved data availability and faster access times, especially in environments with high data traffic.
Fault Tolerance and Continuity
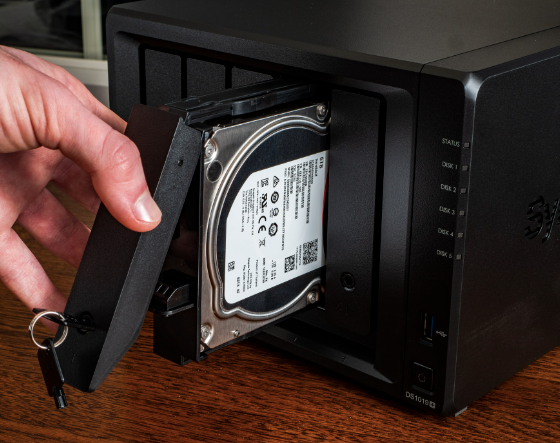
In case of a drive failure, RAID configurations facilitate a seamless transition to a spare drive, ensuring continuity of operations. This fault tolerance, often referred to as hot-swappable drives, minimizes downtime and allows for drive replacement without interrupting the normal operation of the NAS system.
Scalability and Capacity Expansion
RAID configurations provide the flexibility to expand storage capacity as and when required. By adding additional drives to the RAID array, users can easily increase the overall storage capacity without the need to rebuild the entire system or migrate data to a new storage solution.
Performance Optimization
Besides redundancy and fault tolerance, RAID can also optimize performance in NAS configurations. RAID levels such as RAID 0 strip data across multiple drives, resulting in increased performance during read and write operations. This is especially beneficial for tasks involving large file transfers or data-intensive applications.
Overall, RAID plays a critical role in NAS configurations, offering data protection, improved accessibility, fault tolerance, scalability, and performance optimization.