Introduction to Network-Attached Storage (NAS) and Synology
Network-Attached Storage (NAS) provides a centralized data storage solution accessible over a network. Synology, a renowned NAS provider, offers a range of products designed for efficient data storage and management.
Key Features of NAS
- Centralized Storage: Allows multiple users and devices to access and share files from a central location.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Essential for protecting critical data and ensuring business continuity.
- Scalability: NAS systems can easily expand storage capacity to meet growing data demands.
Synology's NAS Solutions
- Diverse Product Range: Synology offers NAS solutions for home users, small businesses, and large enterprises.
- User-Friendly Interface: Synology's DiskStation Manager (DSM) provides an intuitive user experience.
- Advanced Security Features: Includes encryption, two-factor authentication, and antivirus protection.
Overview of File Sharing Protocols in NAS Systems
File sharing protocols are essential in NAS systems, determining how data is accessed and transferred over the network.
Common File Sharing Protocols
- SMB (Server Message Block): Widely used for Windows networks, supporting file sharing, network browsing, and printer services.
- NFS (Network File System): Popular in UNIX and Linux environments, enabling users to access files over a network similar to local storage.
Protocol Selection Factors
- Network Environment: SMB is preferred in Windows-dominated networks, while NFS is favored in UNIX/Linux settings.
- Performance and Security: Each protocol has unique characteristics affecting speed and security.

Detailed Exploration of SMB (Server Message Block) Protocol
SMB Features
- Interoperability: Allows Windows and non-Windows systems to share files.
- Security: Supports encryption and user authentication.
SMB Versions
- SMB 1.0: The original version, now outdated due to security vulnerabilities.
- SMB 2.0 and 3.0: Offer enhancements in performance and security.
In-Depth Analysis of NFS (Network File System) Protocol
NFS Advantages
- Performance: Efficient in handling large files and high-speed data transfers.
- Flexibility: Easily integrates with various operating systems.
NFS Security
- Authentication: NFSv4 includes stronger security features like Kerberos authentication.
- Access Control: Implements permissions and access control lists (ACLs).
Synology's Approach to Network Storage Solutions
Synology integrates multiple file-sharing protocols, including SMB and NFS, to cater to diverse network environments.
Synology's Protocol Support
- Versatility: Supports both SMB and NFS, ensuring compatibility with various devices and operating systems.
- Performance Optimization: Synology optimizes protocols for better speed and reliability.
Synology's Unique Features
- Hybrid RAID (SHR): Simplifies storage management and maximizes data capacity.
- Cloud Integration: Offers seamless integration with various cloud services for backup and synchronization.
In conclusion, Synology provides versatile NAS solutions, supporting both SMB and NFS protocols to accommodate different network environments and requirements. Their commitment to performance, security, and user-friendly interfaces makes them a popular choice for NAS users.
History and Evolution of Synology NAS Devices
Beginnings and Milestones
Synology, founded in 2000, rapidly evolved as a leader in Network Attached Storage (NAS) solutions. Their early focus on user-friendly and reliable storage solutions marked a significant shift in the NAS market. By integrating powerful hardware with versatile software, Synology redefined data storage and management for both personal and business use.
The company's journey includes notable milestones, such as the introduction of DiskStation Manager (DSM), a revolutionary operating system that empowered users with a web-based, intuitive interface for managing their data.
Innovation and Expansion
Over the years, Synology has consistently innovated, improving not only the hardware specifications but also the software capabilities of their devices. They introduced features like high-speed data transfer, robust data protection, and seamless cloud integration. This commitment to innovation ensured that Synology NAS devices remained at the forefront of the industry, catering to a growing demand for efficient and secure data management solutions.
Synology NAS Operating Systems and Software
DiskStation Manager (DSM)
The cornerstone of Synology's software offerings is the DiskStation Manager (DSM). DSM is known for its user-friendly interface, resembling that of a desktop operating system. It offers functionalities like file sharing, data backup, multimedia streaming, and more. DSM's regular updates ensure enhanced security, improved performance, and the introduction of new features, keeping it aligned with evolving user needs.
Additional Software Solutions
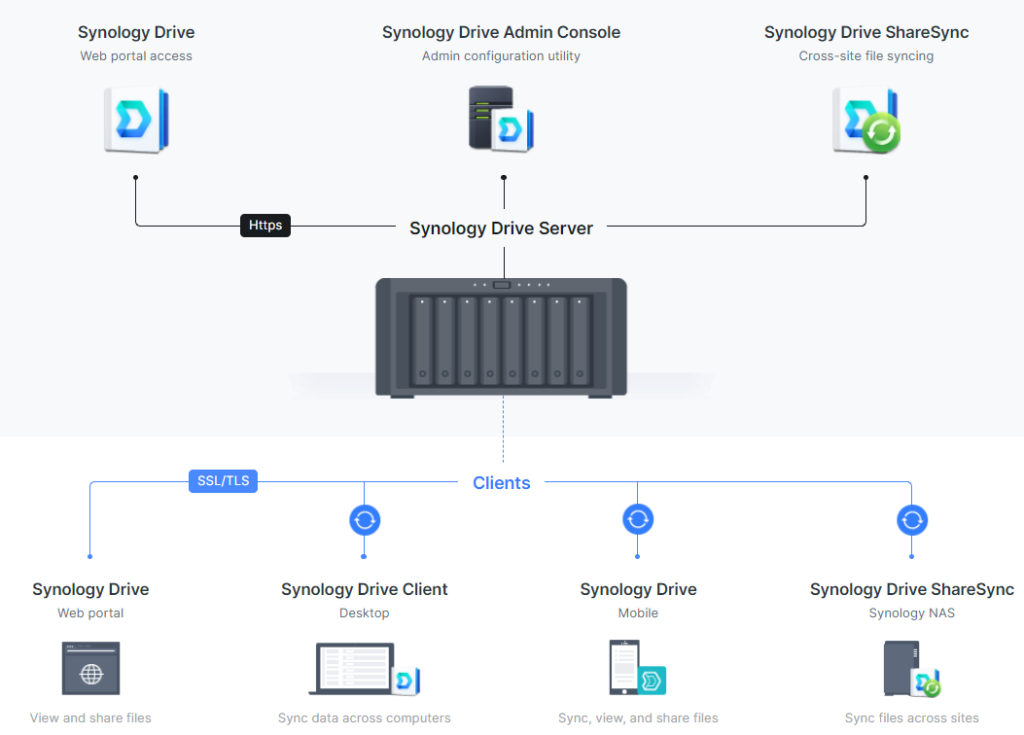
Synology's software ecosystem extends beyond DSM with solutions like Synology Drive, Surveillance Station, and Hyper Backup. Each of these is designed to address specific user requirements, from cloud-based file synchronization to comprehensive surveillance and reliable data backup solutions.

Range of Synology NAS Products and Their Target Audiences
Personal and Home Office Solutions
Synology's range includes models like the DS220j and DS418, which are ideal for personal use and home offices. These models offer a balance of performance and cost, providing essential NAS functionalities like file storage and multimedia streaming.
Enterprise Solutions
For enterprises, Synology offers higher-end models like the RS820+ and DS3617xs. These models are designed for higher performance, offering features like scalable storage, advanced data protection, and virtualization support. They cater to businesses requiring robust data management solutions.
Future Prospects: Blockchain and Beyond
Embracing Blockchain Technology
Synology is poised to integrate blockchain technology into their NAS systems. This integration could offer enhanced data security and decentralized storage solutions. The use of blockchain can lead to improved data integrity, offering a more secure way of storing and managing sensitive information.
Beyond Traditional Storage
Looking beyond traditional storage, Synology is exploring AI-driven data management and IoT applications. These advancements could transform NAS devices into more than just storage units, turning them into central hubs for smart homes and businesses. With the integration of AI, Synology NAS devices could offer predictive analytics, automated data management, and enhanced efficiency in handling large data sets.
Sustainability and Efficiency
In line with global sustainability trends, Synology is focusing on developing energy-efficient NAS solutions. Future devices are expected to be designed with optimized power consumption, reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. This approach aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly technology solutions.
In conclusion, Synology's trajectory from a NAS-focused company to a multifaceted technology innovator highlights its commitment to staying ahead in the data storage and management sector. The integration of blockchain, AI, and IoT, coupled with a focus on sustainability, positions Synology to remain a key player in the future of data management solutions.
Technical Foundations of SMB and NFS
SMB: Server Message Block Protocol
The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, primarily used for providing shared access to files, printers, and serial ports, is a network file sharing protocol. SMB operates as a request-response or client-server protocol, ensuring that client nodes request files and services from a central server.
- Key Features:
- Version History: SMB1 (legacy), SMB2, SMB3 (current version with enhanced security features).
- Operational Mechanics: Works on the application layer and uses TCP port 445.
- Compatibility: Widely compatible with Windows operating systems.
- Security Aspects:
- Encryption: SMB 3.x supports end-to-end encryption.
- Authentication: Integrates with Active Directory for user authentication.
NFS: Network File System Protocol
Network File System (NFS), developed by Sun Microsystems, allows a user on a client computer to access files over a network in a manner similar to how local storage is accessed.
- Key Features:
- Versions: NFSv2 (legacy), NFSv3 (widely used), NFSv4 (enhanced security and performance).
- Operational Mechanics: Operates on the application layer, predominantly using UDP but can also work over TCP.
- Compatibility: Commonly used with UNIX and Linux systems.
- Security Aspects:
- Authentication: Kerberos protocol integration in NFSv4.
- Delegation and ACLs: Advanced access control lists in NFSv4.
Configuring SMB and NFS on Synology Devices
Setting up SMB on Synology
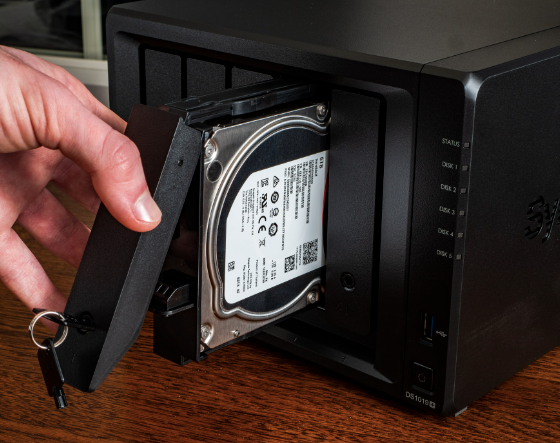
To configure SMB on Synology NAS (Network Attached Storage), users need to access the DSM (DiskStation Manager) interface.
- Steps for Configuration:
- Access Control Panel: Navigate to 'File Services' under the Control Panel.
- Enable SMB Service: Check the option to enable the SMB service.
- Set SMB Protocol Version: Choose the appropriate SMB version for compatibility and security.
Configuring NFS on Synology
Configuring NFS involves similar steps, with specific focus on network permissions and export policies.
- Steps for Configuration:
- Enable NFS Service: In the 'File Services' section, enable NFS.
- Configure Exports and Permissions: Specify the directories to be shared and set appropriate read/write permissions.
Performance and Security Aspects of SMB and NFS
Performance Comparison
SMB and NFS offer different performance characteristics based on network conditions and file operation types.
- Throughput and Latency:
- SMB generally provides higher throughput with Windows clients.
- NFS can offer lower latency in read/write operations, especially in UNIX/Linux environments.
Security Implications
Both protocols have evolved to offer robust security features, but their implementations differ.
- SMB Security: Strong encryption in SMB3, integration with Windows-based authentication systems.
- NFS Security: NFSv4 offers more robust security features, including Kerberos-based authentication.
Future Prospects: Blockchain and Beyond
Blockchain Integration in File Sharing Protocols
The integration of blockchain technology in file sharing protocols like SMB and NFS opens new avenues for security and traceability.
- Immutable Records: Blockchain can provide a tamper-proof record of file access and transfers.
- Decentralized Security: Enhancing traditional centralized security models with decentralized blockchain mechanisms.
Innovations Beyond Blockchain
Looking beyond blockchain, advancements in AI and machine learning offer predictive analytics for network load balancing, potentially increasing efficiency and reducing costs.
- AI-Driven Security: Implementing AI to predict and mitigate security breaches.
- Efficiency Improvements: Machine learning algorithms could optimize data transfer routes and protocol parameters for enhanced performance.
These developments in SMB, NFS, and emerging technologies like blockchain and AI, hold significant promise for the future of network file sharing, providing advancements in security, efficiency, and performance.
Learn more about SMB Learn more about NFS
Common Use Cases for SMB in Synology
Benefits of SMB Protocol
Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) often use Synology's Network Attached Storage (NAS) systems for efficient file sharing and data management. The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol plays a crucial role in these environments. SMB allows multiple users to share files over a network, providing a simple yet powerful interface for accessing and managing data.
Advantages of Using SMB in Synology:
- Easy Integration: SMB seamlessly integrates with existing network infrastructure, requiring minimal configuration.
- High Performance: Offers fast data transfer speeds, essential for businesses dealing with large files.
- Security: SMB includes features for encryption and user authentication, ensuring data security.
- Flexibility: Compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Use Case Scenarios
1. File Sharing and Collaboration: Businesses often use SMB for file sharing, allowing employees to access and collaborate on documents in real-time.
2. Backup and Disaster Recovery: SMB is ideal for creating regular backups of critical business data, providing a safeguard against data loss due to hardware failures or cyberattacks.
3. Media Streaming: SMB can be used to set up a centralized media server, allowing seamless streaming of audio and video files across different devices.
Exploring NFS Applications in Synology Contexts
Understanding NFS
Network File System (NFS) is another protocol used in Synology environments, primarily for system-to-system file sharing. NFS is known for its high performance and compatibility with UNIX and Linux systems.
Key Features of NFS in Synology:
- High Efficiency: NFS provides efficient data access, particularly important for applications requiring high read/write speeds.
- Scalability: Easily scales to accommodate growing data needs, making it suitable for expanding businesses.
- Cross-platform Compatibility: NFS works well with various UNIX and Linux systems, ensuring broad compatibility.
Application Scenarios
1. Centralized Data Storage: NFS is widely used to create centralized storage solutions, simplifying data management and accessibility.
2. Virtualization Environments: NFS is ideal for virtualization setups, allowing multiple virtual machines to access the same storage pool.
3. High-Performance Computing: In high-performance computing environments, NFS facilitates quick data exchange between nodes, essential for complex computational tasks.
Case Studies: Real-World Implementations of SMB and NFS in Synology NAS
SMB Implementation Case Study
Company Profile:
- Industry: Graphic Design
- Size: Medium-sized business
- Challenge: Needed a robust file sharing and collaboration system.
Solution: Implemented Synology NAS with SMB protocol to enable efficient file sharing among team members.
Outcomes:
- Improved Collaboration: Enhanced team productivity with seamless file access.
- Data Security: Increased data security with SMB’s encryption features.
- Reduced Downtime: Minimized downtime with reliable data backup solutions.
NFS Implementation Case Study
Organization Profile:
- Sector: Educational Institute
- Size: Large-scale
- Challenge: Required a high-efficiency data storage solution for research data.
Solution: Deployed Synology NAS with NFS for centralized data storage and easy access for research teams.
Results:
- Enhanced Data Management: Streamlined data storage and retrieval processes.
- Scalability: Successfully accommodated increasing data volumes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced overall storage costs with an efficient NFS setup.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of SMB and NFS protocols in Synology environments, catering to a wide range of business and organizational needs.