The best RAID for NAS depends on specific needs: RAID 0 for speed, RAID 1 or 10 for data security, RAID 5 for a balance, and RAID 6 for extra fault tolerance. Each offers unique benefits, catering to different requirements like performance, storage efficiency, and data protection.
Overview of Common RAID Levels Used in NAS
RAID 0
RAID 0, known for its striping technique, divides data evenly across two or more disks without parity, redundancy, or fault tolerance. This setup excels in speed and storage capacity, making it ideal for tasks that require high read/write speeds. However, if one disk fails, all data is lost. RAID 0 is great for environments where speed is paramount and data loss is not a critical concern.
RAID 1
RAID 1 mirrors data across two or more disks, offering excellent fault tolerance. If one disk fails, the other continues to function, safeguarding your data. This configuration is ideal for critical data storage where data loss is unacceptable. However, it's less efficient in terms of storage capacity since it duplicates data.
RAID 5
Requiring at least three disks, RAID 5 combines striping with parity. It offers a balanced mix of performance, storage efficiency, and data protection. If a single drive fails, the system can rebuild the lost data using the parity information. RAID 5 is well-suited for servers and NAS systems where a blend of performance and data security is needed.
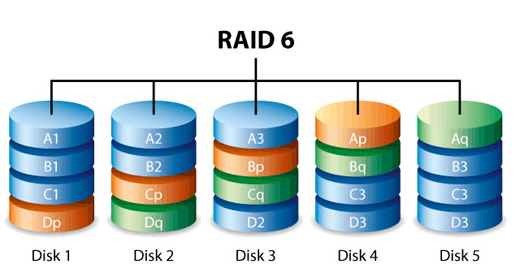
RAID 6
Similar to RAID 5, RAID 6 adds another layer of data protection by using two parity blocks instead of one. It can withstand the failure of two drives simultaneously, offering higher fault tolerance. RAID 6 is a fit for environments where data security is a top priority, although it does sacrifice some storage capacity and speed for this added protection.
RAID 10
Combining the features of RAID 1 and RAID 0, RAID 10 offers both striping and mirroring. It requires at least four disks and provides high performance and data redundancy. RAID 10 is particularly effective in high-availability environments where both performance and data protection are critical. However, the trade-off is lower storage efficiency and higher costs due to the need for more disks.
In terms of RAID technology for NAS systems, these levels present diverse options catering to specific needs, whether it's performance, data protection, or a balance of both. Each configuration has its unique strengths and limitations, making it crucial to assess the specific requirements of your NAS setup before deciding on the RAID level.

Comparative Analysis of RAID Levels for NAS
Performance Comparison
RAID 0 stands out for its exceptional performance, offering the highest read/write speeds due to its striping mechanism. It's ideal for applications that demand quick data access. In contrast, RAID 1 prioritizes data redundancy over speed, making it slower compared to RAID 0. RAID 5 and RAID 6 offer a balance, delivering good performance with the added benefit of data protection. RAID 10 tops the list in performance, combining the speed of RAID 0 and the redundancy of RAID 1.
Data Redundancy and Fault Tolerance
RAID 1, with its mirroring approach, excels in data redundancy, safeguarding data against disk failures. RAID 5 and RAID 6 provide enhanced fault tolerance, with RAID 6 capable of enduring two simultaneous disk failures, a crucial feature for critical data storage. RAID 10 also offers robust fault tolerance, thanks to its mirrored sets.
Storage Efficiency
RAID 0 maximizes storage efficiency as it does not duplicate data. However, RAID 1, RAID 10, and to some extent RAID 5 and RAID 6, sacrifice storage efficiency for data protection. RAID 1 and RAID 10 use double the amount of disk space for the same data, while RAID 5 and RAID 6 use additional space for parity blocks.
Suitability for Different NAS Use Cases
RAID 0 is suitable for non-critical applications where speed is more important than data security. RAID 1 is a go-to for critical data that must not be lost. RAID 5 strikes a balance and is often the choice for small to medium-sized business NAS setups. RAID 6, with its higher fault tolerance, suits environments where data loss can have severe consequences. RAID 10, offering the best of both worlds, is ideal for high-end NAS solutions where both performance and data safety are top priorities.
This comparative analysis reveals that each RAID level has specific strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different NAS scenarios. The choice hinges on individual needs for performance, data redundancy, storage efficiency, and the specific use case of the NAS system. Understanding these aspects helps in making an informed decision tailored to the specific requirements of your NAS setup.
Factors to Consider When Choosing RAID for NAS
Size of the NAS Setup
The size of your NAS setup plays a critical role in choosing the right RAID. For smaller setups, RAID 1 or RAID 5 often suffices, offering a good balance between cost and performance. Larger setups might benefit more from RAID 6 or RAID 10, providing better fault tolerance and performance, essential for managing more substantial data volumes.
Data Security Needs
Data security is paramount in any NAS setup. RAID 1 and RAID 10 offer high data security through mirroring, making them ideal for sensitive data. RAID 5 and RAID 6 provide data protection with parity but at the cost of some storage space. RAID 0, lacking redundancy, is not suitable for critical data.
Performance Requirements
For high-performance needs, RAID 0 and RAID 10 stand out. RAID 0, with no data protection overhead, offers the highest speeds, suitable for tasks requiring rapid data access. RAID 10 combines speed with data protection, making it ideal for high-performance, high-security environments.
Budget Constraints
Budget is a crucial factor. RAID 1 and RAID 5 are cost-effective, providing a balance of performance and redundancy without needing many drives. RAID 10 and RAID 6, offering higher data protection, require more disks, leading to higher initial costs and maintenance expenses.
Storage Efficiency
RAID levels also vary in their storage efficiency. RAID 0 utilizes 100% of the disk space, but at the risk of data loss. RAID 1 and RAID 10 offer high data protection but halve the storage capacity. RAID 5 and RAID 6 provide a middle ground, sacrificing some storage for parity data but still offering more efficient use of disk space compared to RAID 1 or RAID 10.
Longevity and Maintenance
Longevity is another key factor. RAID setups with redundancy (RAID 1, 5, 6, 10) often have longer lifespans as they can withstand disk failures. However, this also implies a need for regular maintenance and monitoring to replace failed drives and manage the RAID array.
Each of these factors plays a pivotal role in determining the most suitable RAID level for a NAS system. Balancing these considerations helps ensure that the selected RAID configuration aligns well with the specific needs, budget, and goals of the NAS deployment. Careful consideration of these aspects ensures optimal performance, data security, and cost-effectiveness of the NAS system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Popular RAID Levels in NAS
Pros and Cons of RAID 0
- Advantages:
- High Speed: Offers the highest data transfer rates.
- Maximum Storage Utilization: Utilizes 100% of disk space without redundancy overhead.
- Ideal for Non-Critical Data: Best for systems where speed is more important than data security.
- Disadvantages:
- No Data Redundancy: A single disk failure results in total data loss.
- Not Suitable for Critical Data: Due to lack of redundancy, it's risky for storing vital information.
Pros and Cons of RAID 1
- Advantages:
- Excellent Data Protection: Mirroring ensures data safety even if one disk fails.
- Simple to Implement: Easy to set up and manage.
- Good Read Speed: Offers improved read performance.
- Disadvantages:
- Reduced Storage Capacity: Only 50% of total disk capacity is usable.
- Higher Cost per GB: Requires double the disk space for the same amount of data.
Pros and Cons of RAID 5
- Advantages:
- Balanced Performance and Security: Combines good speed with data protection.
- Efficient Storage Use: More storage-efficient than RAID 1.
- Single Disk Redundancy: Can survive a single disk failure.
- Disadvantages:
- Complexity: More complex to manage than RAID 1.
- Slower Write Speeds: Due to parity calculations.
Pros and Cons of RAID 6
- Advantages:
- High Fault Tolerance: Can handle two simultaneous disk failures.
- Suitable for Large Arrays: Ideal for setups with many drives.
- Data Protection: Offers robust data security.
- Disadvantages:
- Reduced Storage Efficiency: Two disks' worth of space used for parity.
- Complexity and Cost: More complex and expensive to implement than RAID 5.
Pros and Cons of RAID 10
- Advantages:
- Excellent Performance: Combines the speed of RAID 0 with the redundancy of RAID 1.
- High Data Redundancy: Very secure against disk failures.
- Good for Critical Applications: Ideal where both speed and data security are vital.
- Disadvantages:
- Costly: Requires at least four disks, making it more expensive.
- Storage Efficiency: Only 50% of total storage capacity is usable.
These RAID levels each have unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different NAS applications. RAID 0 excels in speed but lacks in data security, while RAID 1 focuses on data protection at the expense of storage efficiency. RAID 5 offers a balance of speed and security, RAID 6 adds an extra layer of data protection, and RAID 10 provides the best of both worlds at a higher cost and reduced storage efficiency. Selecting the right RAID level involves evaluating these pros and cons against the specific needs and constraints of your NAS setup.
Case Studies: Real-world NAS Implementations with Different RAID Configurations
Home NAS Solutions
- Scenario: A home user seeking a balance between media streaming performance and data security for family photos and documents.
- RAID Choice: RAID 1.
- Reason: Offers redundancy to protect against data loss, crucial for irreplaceable family memories.
- Implementation: Two 4TB drives provide a safe, mirrored storage solution.
- Outcome: Efficient media streaming with the peace of mind that personal data is secure.
Small Business NAS Setups
- Scenario: A small business needing to store critical business data with a balance of performance and data protection.
- RAID Choice: RAID 5.
- Reason: Provides a blend of storage efficiency, performance, and data protection.
- Implementation: Four 8TB drives, yielding 24TB of usable storage with fault tolerance.
- Outcome: Effective handling of daily business operations and data safety, ensuring business continuity.
Enterprise NAS Systems
- Scenario: An enterprise requiring a high-performance, high-capacity storage solution for critical applications.
- RAID Choice: RAID 10.
- Reason: Offers high-speed access and excellent redundancy for critical enterprise data.
- Implementation: Eight 10TB drives, providing 40TB of fast, mirrored storage.
- Outcome: Superior performance for demanding applications, with robust data protection ensuring minimal downtime.
Each of these scenarios showcases a different RAID level, selected to meet specific needs in terms of performance, storage efficiency, and data security. Home NAS solutions often prioritize data protection on a smaller scale, making RAID 1 an ideal choice. Small businesses, balancing cost with performance and data safety, find RAID 5 fitting. For enterprises where performance and data security are paramount, RAID 10 stands out as the best solution, albeit at a higher cost. These case studies demonstrate the practical application of RAID technology in NAS setups, highlighting the importance of aligning RAID configurations with specific use cases and requirements.

